Table of Contents
- What is Azure Storage?
- How to create an Azure Storage Account
- Video Tutorial
WHAT IS AZURE STORAGE
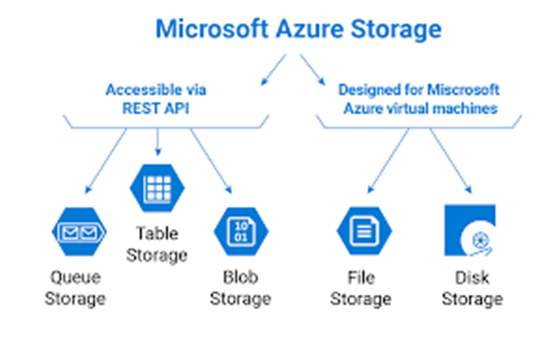
Azure storage provides storage that is highly available, secure, durable, scalable, and redundant. Azure storage offers five different types of storage that are further broadly classified into two main headings each of which has five subheadings in total. They are as follows –
On the basis of – Accessible via REST API
- Queue Storage
- Table Storage
- Blob Storage
On the basis of – Designed for Microsoft Azure virtual machines
- File Storage
- Disk Storage
HOW TO CREATE AN AZURE STORAGE
The process is divided into four broad steps which are Basics, Networking, Advanced, Tags and Review & Create.
BASICS
Go to the Azure portal. https://azure.microsoft.com/en-in/features/azure-portal/
On the left side drop down menu bar, there will be an option called ‘Storage Accounts’.
If this option is not available on certain browsers, there are various other ways to access storage accounts.
- Click on the option called ‘Create Resource’ on the same left side dropdown menu.
- The term ‘Storage Account’ can be searched on the search bar given at the top of the Azure portal.
To make a new storage account, click on the + symbol at the top left corner of the task bar.
The first thing that will be required is to choose the subscription option. A user will need to have a valid subscription in order to create a new storage account.
Then, the research group under which the storage account will be created needs to be specified in the next step.
Next, a name must be created for the storage account that should be unique across all the existing storage accounts in Azure. It must also be 3 to 24 characters long and can contain only lowercase numbers and letters.
Next, the location where the storage accounts are to be created in must be specified. There are 40 plus options consisting of locations from all over the world that is available to choose from.
Performance – The storage accounts are available in two options which are Standard and Premium. Standard Storage Accounts are backed by magnetic drives and provide the lowest cost per GB. Premium Storage Accounts are backed by solid-state drives and are best for I / O intensive applications. Premium Storage for all disks qualifies for a 99.9 % SLA and charged more than the Standard Storage Accounts.
The next step is to choose the kind of account that the user wants to create. There are five different types of storage that we have already discussed above. One must be chosen from the five options.
The replica must be decided in the next step of the process which determines how the user wants to replicate the data. There are couple of options such as LRS, ZRS and GRS.
- LRS – Locally Redundant Storage
- ZRS – Zone Redundant Storage
- GRS – Geo Redundant Storage
If LRS is selected, Microsoft will keep the storage account in one of the data centres with relevance to the location provided and will be replicated within the location. ZRS is within a data center where they have a different power supply, pooling, and network.
A GRS will replicate the data into the nearest pairing region. Definitions for Pairing Regions have been given on another separate post on the Azure portal which can be accessed to learn further about this topic. Assuming that the location chosen was East US, then the default pairing region will be West US and vice versa. If UK West has been chosen, then the pairing region will be UK South.
NETWORKING
The access tier (Hot / Cool) must then be chosen accordingly following which the network connectivity will have to be chosen. Hot access tiers are used when the user access the data in a highly frequent manner.
On the other hand, if the storage account has been created for an archival purpose, then the Cool tier can be used. This is one of the factors that are taken into account when determining the charges placed for the storage account.
The hot accounts are charged higher for the GB data storage. The cool accounts’ data storage costs are less whereas the costs per transaction of data are higher.
Advanced:
- The advanced storage account creation settings consist of the following features that can be either Enabled / Disabled
- Security
- Azure Files
- Data Protection
- Data Lake Storage Gen2
Tags:
Tags can be created in order to identify the purpose of the storage accounts. For example, the type of application or environment that will be used in the storage account is selected in this next step.
Review & Create :
The final step is the review and creation of the storage account. It will take a while to create the storage account. The deployment will be under process and once it has been approved, it will be visible and ready to be used.
Under the overview tab Containers, File Shares, Tables and Queues can be created.
Video Tutorial